We Use CookiesWe use cookies to enhance the security, performance,
functionality and for analytical and promotional activities. By continuing to browse this site you
are agreeing to our privacy policy
10 Best Microscopes
From leading brands and best sellers available on the web.By clicking on a link to a third party's website, log data is shared with that third party.
Buying Guide for the Best Microscopes
Choosing the right microscope involves understanding your specific needs and the features that will best meet those needs. Whether you're a student, a hobbyist, or a professional, the right microscope can enhance your ability to observe and analyze specimens. Consider what you will be using the microscope for, the level of detail you need, and how often you will be using it. This will help you determine which features are most important for your purposes.MagnificationMagnification is the process of enlarging the appearance of an object. In microscopes, this is achieved through a combination of lenses. The total magnification is the product of the eyepiece magnification and the objective lens magnification. For basic educational purposes, a magnification of 40x to 400x is usually sufficient. For more detailed work, such as in biology or materials science, you might need a microscope with a magnification of 1000x or more. Consider what level of detail you need to see in your specimens to choose the right magnification.
ResolutionResolution is the ability of a microscope to distinguish two close points as separate entities. It determines the clarity and detail of the image. Higher resolution allows you to see finer details. For general use, a standard resolution is adequate, but for detailed scientific research, a higher resolution is necessary. Think about the level of detail you need to observe in your specimens to decide on the resolution you require.
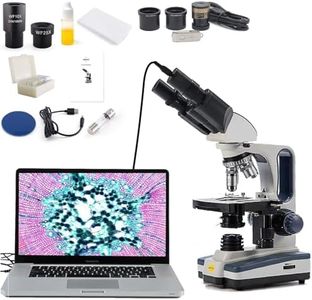
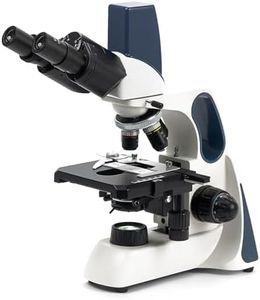
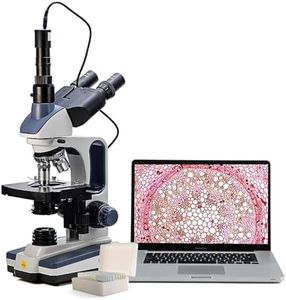
Type of MicroscopeThere are several types of microscopes, including compound, stereo, digital, and electron microscopes. Compound microscopes are ideal for viewing small, thin specimens like cells. Stereo microscopes are better for larger, three-dimensional objects. Digital microscopes connect to a computer for easy viewing and sharing. Electron microscopes offer extremely high magnification and resolution for very small specimens. Consider the type of specimens you will be observing to choose the right type of microscope.
IlluminationIllumination refers to the light source used to illuminate the specimen. Proper lighting is crucial for clear viewing. Microscopes can have built-in LED, halogen, or fluorescent lights. LED lights are energy-efficient and long-lasting, while halogen lights provide bright, white light. Fluorescent lights are used for specific applications. Consider the environment in which you will be using the microscope and the type of specimens you will be observing to choose the appropriate illumination.
Stage and FocusThe stage is the platform where the specimen is placed, and focus refers to the mechanism that adjusts the clarity of the image. A mechanical stage allows for precise movement of the specimen, which is useful for detailed work. Coarse and fine focus adjustments help in achieving a clear image. For basic use, a simple stage and focus mechanism may suffice, but for more detailed work, a mechanical stage and fine focus are beneficial. Consider how precise you need to be in observing your specimens to choose the right stage and focus features.





![[Research-Grade] Vabiooth Lab Compound Trinocular Microscope 40X-2500X Magnification with 7" LCD Screen 5MP E-Eyepiece, Two-Layer Mechanical Stage for Animal Husbandry, Pet Hospitals, Lab, Farms](https://images-proxy.bestreviews.guide/ixsX4l19ay9YM6HUDvEcBe64-Ig=/0x300/https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/41B0xuId-LL._AC_CX679_.jpg)